Who doesn’t love pancakes?
Pancakes are
- delicious,
- sweet,
- chocolat-y (this depends on your taste),
- and an application of stack data structure in real life.
The top-to-bottom approach is the conventional way to eat pancakes. Plus, you can only apply butter, chocolate, or maple syrup to the top one. This is analogous to the stack data structure. You can only pop (remove) pancakes one-by-one from the top; and peek (look at) the topmost element only.
.
From now on, I will use the term “stack” to refer to the stack data structure.
There are two ways (that I know of) to implement stack using C: arrays and linked list. This post only covers the former
First define the maximum size of the stack. Since we’re using arrays, this size is fixed, so there are no dynamic memory allocation involved here.
#define MAX 8
Then declare the array using above value in C. We will also need another variable “top” to keep track of the index of the topmost element.
int stack[MAX];
int top = -1;
Why do we use -1? This is not python where you can use negative index to refer to the last element.
True. -1 is simply the intial value. Later when we add elements starting from index 0, the “top” variable will be incremented by 1 so it “points” to the first element. If a second element is added, increment again. If the second element is remove, decrement the “top” variable.
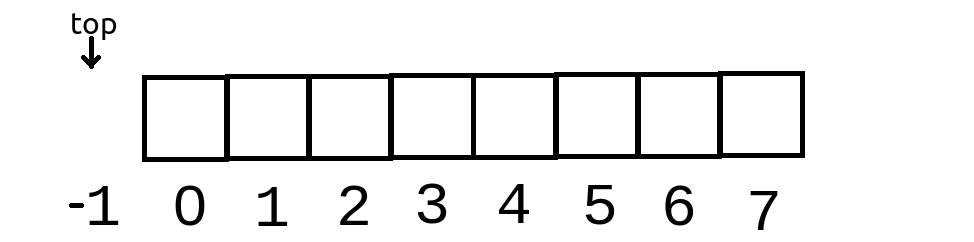
So for now we have an empty array with size 8.
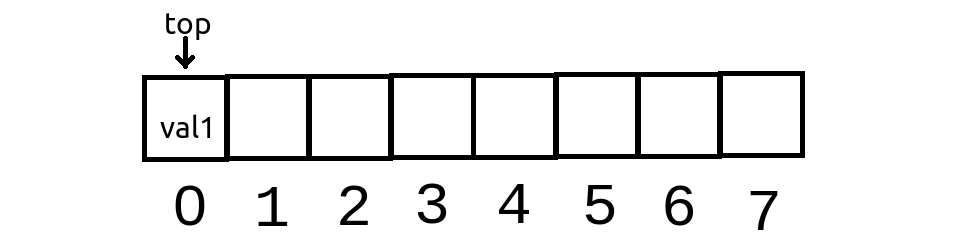
To push something onto the first element of the array. The algorithm is very simple: ask user for the value, finally increment the “top” variable by one, adn replace the array element with the value. So
int val;
printf("%s", "Please enter a value to be pushed into the stack");
scanf("%d", "&val)
top++; //change value from -1 to 0
stack[top] = val; //add the value to the first element of the array (index 0)
Now, we need to add an exception when the array is already full (or top = MAX-1. Remember, top is only the index, so we need to substract one from MAX value to get the highest possible index. So
if top == MAX - 1 {
puts("The stack is full");
//place the return statement here
}
else {
//put the previous codes here
//
}
So now we have the value as the first element in the array and the top variable will point to it.
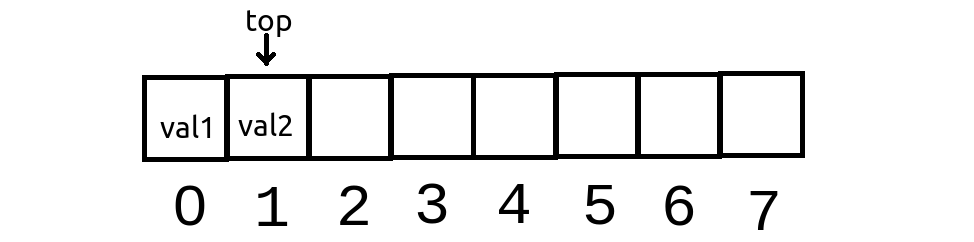
If we repeat the above code, the “top” value will be incremented to 1 and the so the second value inserted will take the place of element at index 1. Hence
Done for the push() function.
For the pop function, it’s actually very very simple. Just point the “top” variable to the next-in-stack element. Yes, we don’t do anything to the topmost element; it’s going to be overwritten later anyway.
if top == -1 {
puts("The stack is empty");
//place the return statement here
}
else {
//top--;
//
}
Same thing goes for the peek function, we only need to call the “top”-th element in the stack. So
if top == -1 {
puts("The stack is empty");
//place the return statement here
}
else {
//printf("%d", stack[top];
//
}
.
The implementation using array is very simple.

Leave a comment